KDM4
A Powerful Regulator of Gene Transcription
KDM4 is a family of histone demethylases that govern gene control by removing methyl groups from histones, and thereby regulating the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors. This can influence which genes are turned on or off as well a their level of expression.
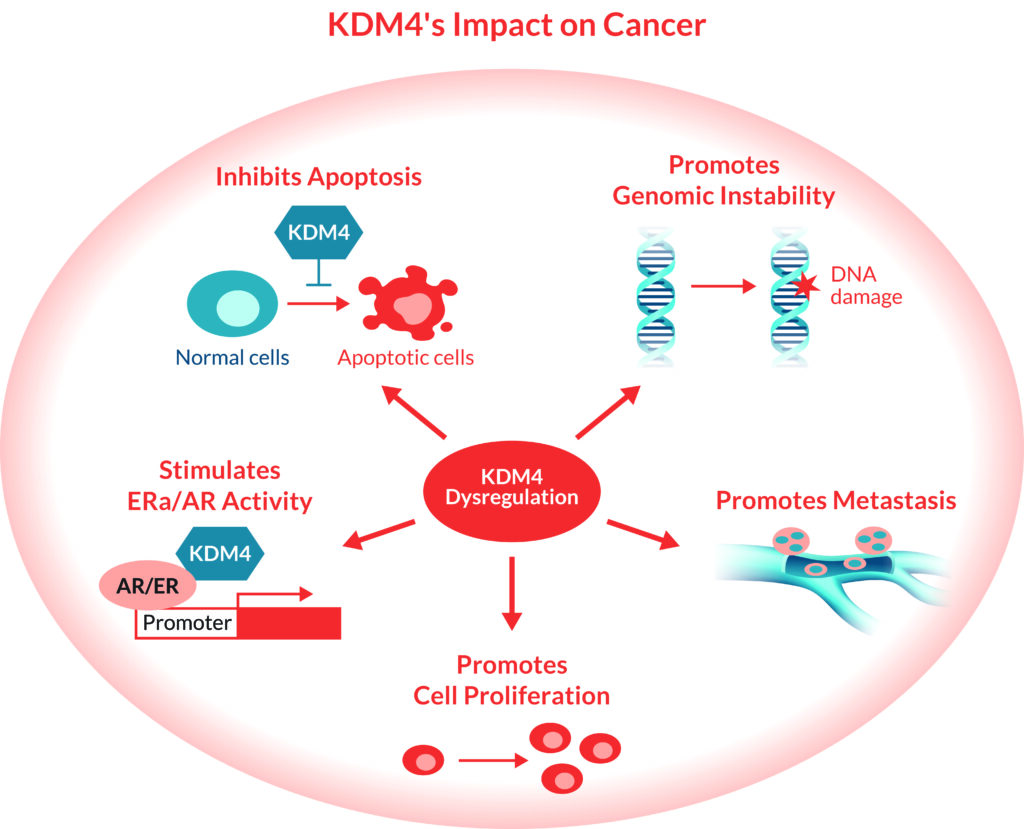
In cancers, KDM4 has emerged as a well-recognized anti-cancer target due to its ability to drive tumor growth, as well as tumor resistance to therapies, by regulating critical signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation, cancer stem cell maintenance, evasion of apoptosis, deficient DNA repair, metastasis, and stimulation of certain hormones.
The KDM4 family consists of four major isoforms (KDM4 A, B, C, and D). Functional redundancy and cross-activity has been observed across these isoforms, therefore, inhibition of one has been shown to to be ineffective. Pan-inhibition targeting multiple or all KDM4 isoforms is required to fully suppress KDM4 function. Tachyon’s TACH101 is the only pan-KDM4 inhibitor that is in clinical development. A multicenter Phase 1 study of TACH101 for the treatment of advanced or metastatic cancers is currently underway (NCT05076552).